2. Platform
MSD’s electrochemiluminescence detection technology uses SULFO-TAG™ labels that emit light upon electrochemical stimulation initiated at the electrode surfaces of MULTI-ARRAY® and MULTI-SPOT® microplates.
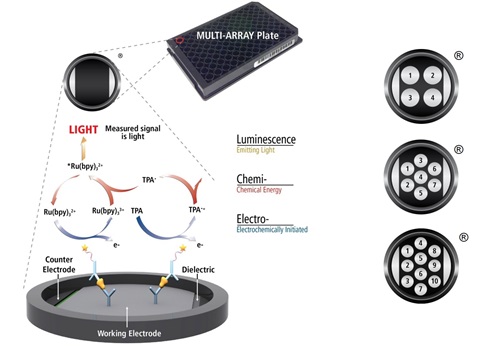
Electrochemiluminescence Technology
- Minimal non-specific background and strong responses to analyte yield high signal-to-background ratios.
- The stimulation mechanism (electricity) is decoupled from the response (light signal), minimizing matrix interference.
- Only labels bound near the electrode surface are excited, enabling non-washed assays.
- Labels are stable, non-radioactive, and directly conjugated to biological molecules.
- Emission at ~620 nm eliminates problems with color quenching.
- Multiple rounds of label excitation and emission enhance light levels and improve sensitivity.
- Carbon electrode surface has 10X greater binding capacity than polystyrene wells.
- Surface coatings can be customized.
3. Method
S-PLEX® assays use either S-PLEX 96-well SECTOR™ or QuickPlex® plates that are coated with streptavidin. These plates provide high sensitivity, consistent performance and excellent inter- and intra-lot precision. S-PLEX kits are supplied with biotinylated capture antibody, a TURBO-BOOST® conjugated detection antibody, a calibrator, assay and antibody diluents, and S-PLEX specific reagents.
The S-PLEX assay protocol is simple, robust and executed in three steps: Assemble, Enhance, and Read as illustrated below. Representative calibration curve, high, mid, and low quality controls (HQC, MQC and LQC) data for pT217 and pT181 assays across 20 runs by multiple analysts over multiple days are shown and demonstrate S-PLEX assay robustness.
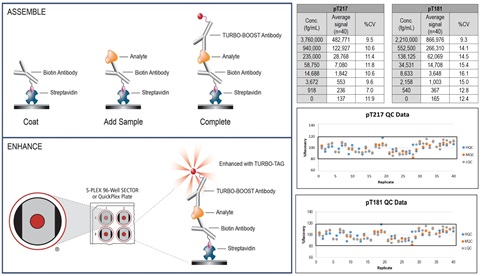
4. Results
a. Accuracy, Precision & Sensitivity
Inter-assay (between runs) and intra-assay (within runs) accuracy and precision were assessed by performing 6 runs on 4 different days by 4 different analysts. Each run consisted of calibration curve, diluent QCs (HQC, MQC, LQC), matrix QCs (EQC1-EDTA plasma, EQC2-Serum, EQC3-CSF), and upper and lower limit of quantitation samples (ULOQ, LLOQ) tested in duplicate. The pT217 and pT181 assays demonstrated good accuracy and precision. Inter-assay and intra-assay accuracy and precision for diluent and matrix QC samples were ±20% and <20%, respectively. Samples prepared at the ULOQ and LLOQ exhibited within and between run precision of ≤25%, accuracy of 75-125% and total error (measurement of bias) of ≤40%. LLOQ represents assay sensitivity.

b. Dilution Linearity & Prozone Effect
Good dilution linearity (%recovery range ±20%) was observed between neat to 8-fold dilutions in CSF and serum, and 2- to 8-fold dilutions in EDTA plasma across the two assays. A slight matrix effect was observed in neat EDTA plasma samples.
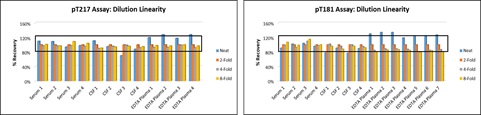
No prozone effect was observed in any of the matrices. Sample concentrations above ULOQ are labeled as ALQ (above limit of quantitation).

c. Specificity
The pT217 and pT181 assays showed no impact on sample quantitation upon addition of non-phosphorylated tau protein. The addition of tau protein containing a T217 – A217 mutation also did not interfere with the pT217 assay. As expected, over-recovery was observed for the pT181 assay in the presence of the mutated protein, which is partially phosphorylated at the T181 site.
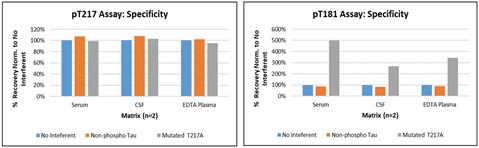
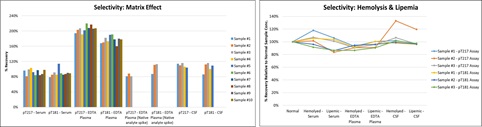
d. Selectivity
Selectivity was assessed by spiking calibrator in human serum (n=10), EDTA plasma (n=10), and CSF (n=5) samples. There was no discernable matrix effect in serum and CSF: >80% of samples recovered within ±20% across both assays. Over-recovery was observed in calibrator-spiked EDTA plasma samples due to the nature of the recombinant calibrator. Recovery within ±20% was obtained with spiked native analyte (high CSF sample) in EDTA plasma samples. Both assays are tolerant to hemolysis and lipemia.
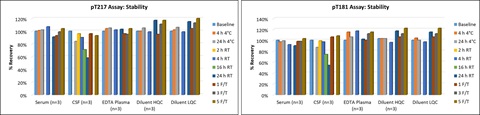
e. Stability
Samples (human serum, EDTA plasma and CSF) were analyzed after being subjected to storage at RT (23°C ± 2°C) or 2-8°C for 4 and 24 hours, or subjected to 1, 3 or 5 freeze-thaws cycles. The data indicates that all samples are stable, with percent recoveries within ±25% of baseline sample concentrations and precision ≤20%, through storage at RT for 24 hours (except for CSF), 2-8°C for 24 hours and up to 5 freeze-thaw cycles. CSF is stable for 4 hours at RT.
f. Sample Testing
Two sets of samples were tested neat in duplicate to evaluate pT217 and pT181 levels in human serum, EDTA plasma, and CSF. Data are shown for all samples with pTau levels above the assay limits of detection. Higher levels of pT217 and pT181 were observed in cognitively impaired (CI) donors with higher MMSE scores compared to healthy donors.

- Sample set 1 are matched human serum, EDTA plasma, and CSF samples from 15 healthy/control donors and 15 CI donors. MMSE score range for Control donors is 28-30 and for CI donors is 16-23.
- Sample set 2 are serum samples from 9 healthy/control donors and 23 CI donors. MMSE score range for CI donors is 4-23.
5. Conclusion
Novel ultrasensitive assays were validated for detection of phosphorylated tau (pT217 and pT181). The assays allow for accurate and precise quantitation of pT217 and pT181 in human serum, EDTA plasma, and CSF. The assays were validated in MSD’s Bioanalytical Laboratory, which is GLP-compliant and provides preclinical and clinical sample testing services.